5G Handover is a very important feature in 5GNR systems (5G New Radio). 5G has come close to standardization with many news from Verizon and T-Mobile regarding deployments and acquisitions specially with NOKIA.
- NOKIA inks deal with T-Mobile for $3.5B (Press Release)
- Verizon and Nokia competete 5G NR Mobility Call (Press Release)
I personally have a patent that covers both X2 and XN Handover:

4G LTE
In the 4G LTE System, we would have an ENodeB, MME, S-GW, PDN-GW, as common elements of the network, hence the X2 and S1 interfaces were used for handover.


In this design, X2 handover facilitates handoff between eNodeBs and relies on the MME for S1-AP handoff only.
In 5G, things have changed a bit:
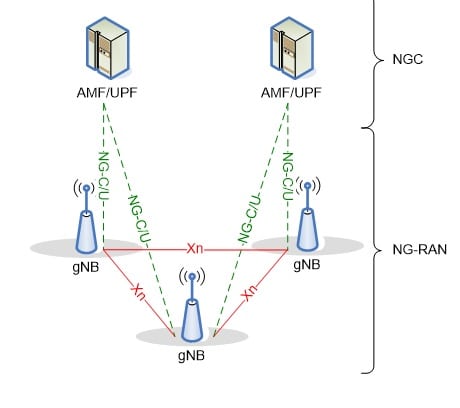
Ad as shown in the figure, the gNB has other entities and interfaces such as ch Xn interface, NG-C/U, and in the infrastructure called (NGC) no longer (EPC) we observe the AMF/UPF duality that resembles the MME/S-GW on LTE.
In comparison, UEs are the same, different radios, on one end LTE, and into the future a 5G radio.
What are the main actors for handover on LTE
- eNodeB – or the Base Station, contains the RF and all IP-level connectivity to the MME/S-GW/PDN-GW to create and maintain connectivity between the RF and EPC-Bearer or Tunnels to the outside world.
- S-GW: Refers to a component that connects the eNodeB with the PDN-GW and is usually a router that sends the tunnel to the PDN-GW with data from the eNodeB or the UE
- PDN-GW: Functions as the anchor or the home of the network, is the main NAT/Routing GW to the internet and keeps track of all tunnels for each UE on the network, and knows how to forward packets to the UEs.
- MME: The Mobility Management Entity, handles mobility in general, required for the S1-AP handover, and handles many mobility functions coordinating with the PDN-GW/S-GWs.
There are multiple specifications related to handover on LTE and defined by ETSI/3GPP organizations.

5G Systems
There are also several other components as follows:
- gNB : Refers to the Base Station, like in the old LTE, the eNodeB
- NR: Refers to the “New Radio” technology
- NG-RAN: NG-RAN is Next Generation Radio Access Network. This consists of gNB and ng-ENB.
- AMF Access and Mobility Management Function AF Application Function
- UPF User Plane Function
- NGC: Next Generation Core
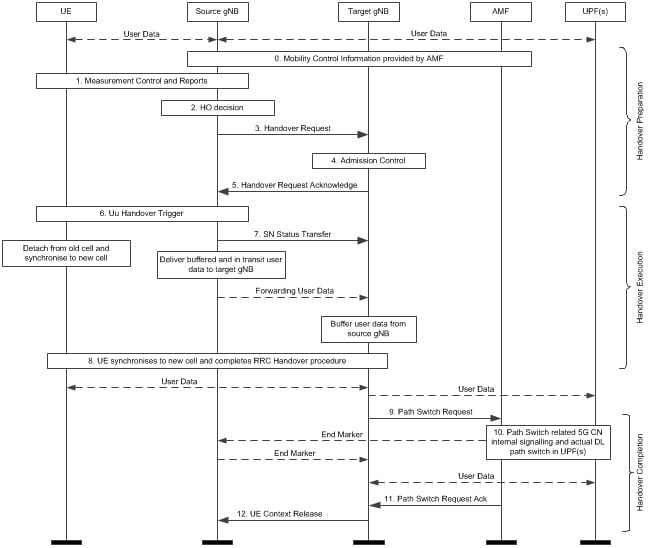
There in 5G the handover is called Xn Handover
- As the UE sends the measurement reports and the Source gNB detects that a handover is required, then it connects with the Target gNB to start a switch
- The UE does a handover and connects to theTarget gNB That has already switched the tunnels to the target
- The UE forwards as part of the handover process, This is called RRC
The NG-RAN sends the UE Notification message to report the current RRC state for the UE (i.e. RRC Inactive state or RRC Connected state). The current UE location information (i.e. TAI + Cell Identity) is always included when RRC state information is reported.
- Thru this, the UE can then handoff fast and all the data is available for you.
How is this different from the X2 Handover
The differences between LTE handover (X2, S1) and 5G Handover (XN, N2) are subtle, and the main difference is that the X2 handover. We server that Location Information is mandatory, but it was after LTE
Rel-13 as well. The changes are minimum and this facilitates the understanding of all functions including AMF / UPF in 5G. In TS 38.423 V.15, the Xn-AP commands are shown, which is a similar document to the X2-AP specification.
If the Location Reporting InformationIE is included in the HANDOVER REQUEST message, then the target NG-RAN node should initiate the requested location reporting functionality as defined in TS 38.413 [5].
Similarly this is shown in TS 123.502 with
- Target NG-RAN to AMF: N2 Path Switch Request (List of PDU Sessions To Be Switched with N2 SM Information, List of PDU Sessions Rejected with a rejection Cause per PDU Session, UE Location Information)
